
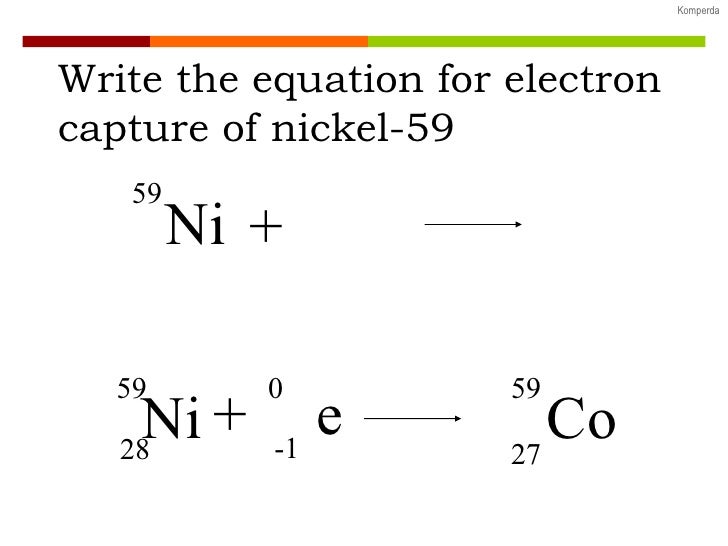
N-acetylaspartate (NAA) peak: resonates at 2.0 ppm.glutamine-glutamate peak: resonates at 2.2-2.4 ppm.gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) peak: resonates at 2.2-2.4 ppm.2-hydroxyglutarate peak: resonates at 2.25 ppm.arterial spin labeling (ASL) MR perfusion.dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) MR perfusion.dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC) MR perfusion.metal artifact reduction sequence (MARS).turbo inversion recovery magnitude (TIRM).fluid attenuation inversion recovery (FLAIR).diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tractography.MRI pulse sequences ( basics | abbreviations | parameters).iodinated contrast-induced thyrotoxicosis.iodinated contrast media adverse reactions.clinical applications of dual-energy CT.as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA).Typically, it occurs in heavy nuclei with a relative abundance of protons or where insufficient decay energy exists for positron emission to occur 3. These transitions may result in the loss of an outer orbital electron, where it is ejected as an Auger electron.Įlectron capture is rarely an exclusive decay mode and typically occurs alongside beta-plus decay within the radioactive sample. Electron Capture An alternate way for a nuclide to increase its neutron to proton ratio is by a phenomenon called electron capture. The vacancy left by this electron is then filled by an outer orbital electron setting off a cascade of electron transitions with their associated characteristic x-rays emission. A continuous spectra of Bremsstrahlung is radiated as the inner shell electron is propelled towards the nucleus. The electron capture decay pathway is usually associated with several other processes. The decay energy is almost wholly transferred to the emitted neutrino with a characteristic quanta of energy. The decay pathway has similarities to beta decay and is often termed inverse beta decay 2. What is the ground-state electron configuration of the potassium ion. Note the reduction in atomic number but conservation of mass number in the daughter nucleus. 9 Write the symbol or formula (including charges) for each of the following ions. The electron on the left side of the equation is usually absorbed from the K or L shell of the parent nucleus. Proton-deficient nuclei undergo beta decay - emitting a beta particle (electron) and an antineutrino to convert a neutron to a proton - thus raising the elements atomic number Z by one.The nuclear reaction depicting electron capture decay is: Proton-deficient or neutron-deficient nuclei undergo nuclear decay reactions that serve to correct unbalanced neutron/proton ratios. Write down the - decay equation and determine the maximum kinetic energy of the electrons emitted.

Other heavy unstable elements undergo fission reactions in which they split into nuclei of about equal size. Alpha decay is a form of spontaneous fission, a reaction in which a massive nuclei can lower its mass and atomic number by splitting. The energy released in an alpha decay reaction is mostly carried away by the lighter helium, with a small amount of energy manifesting itself in the recoil of the much heavier daughter nucleus. In EC decay the energy release Q is given entirely to the emitted neutrino (), so monoenergetic neutrinos are emitted in EC decay.
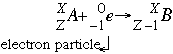
Therefore, the mass of the parent atom must simply be greater than the sum of the masses of its daughter atom and the helium atom. Since the number of total protons on each side of the reaction does not change, equal numbers of electrons are added to each side to make neutral atoms. \( \newcommand\]Īs with beta decay and electron capture, Δm must only be less than zero for spontaneous alpha decay to occur.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
